Introduction
When Elon Musk unveiled the Tesla Bot concept at Tesla’s AI Day in August 2021, many skeptics dismissed it as yet another ambitious Musk project that would struggle to materialize. Just three years later, the robot now known as Optimus has evolved from a person in a spandex suit to functioning prototypes demonstrating increasingly sophisticated capabilities. This blog explores Tesla’s ambitious foray into humanoid robotics, the technical challenges involved, and the potential impact on industries and everyday life.
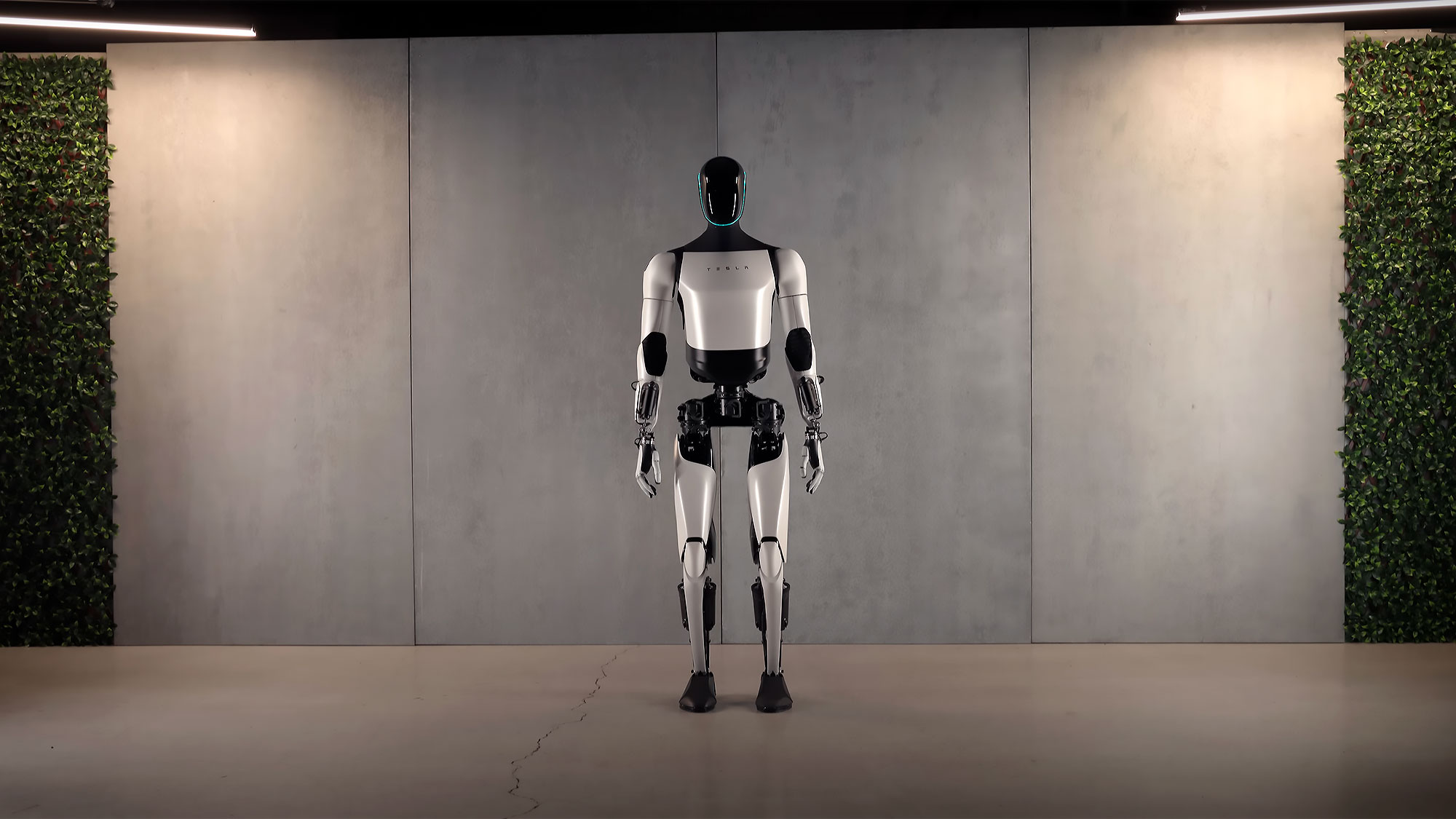
The Evolution of Optimus
From Concept to Reality
Tesla’s journey with Optimus began with a dramatic announcement featuring a person in a robot costume dancing on stage. This theatrical introduction belied the serious engineering challenge Tesla was undertaking. By September 2022, Tesla revealed its first actual prototype, nicknamed “Bumble C.” Though basic in functionality, it could walk unassisted and perform simple tasks.
The following year, Tesla demonstrated significant advancements with newer prototypes. By 2024, Optimus had evolved to incorporate more refined movements, improved dexterity, and enhanced cognitive abilities powered by Tesla’s neural networks.
Technical Specifications
The Optimus robot stands approximately 5’8″ (173 cm) tall and weighs around 125 pounds (57 kg). This size was deliberately chosen to be non-threatening while still capable of navigating human environments and performing useful tasks. Key features include:
- Power System: Built with Tesla-designed battery technology, providing several hours of operation
- Movement: 28+ degrees of freedom through actuators designed in-house
- Vision: 8 cameras using the same computer vision system developed for Tesla vehicles
- Processing: Custom Tesla AI chips similar to those used in Tesla’s Full Self-Driving computer
- Hands: Five-fingered hands with independent movement, capable of precise manipulation
- Materials: Lightweight alloys and composites for durability and safety
The Technical Challenge
Creating a general-purpose humanoid robot presents challenges that go far beyond automotive engineering. Tesla has had to innovate in several areas:
Actuators and Movement
Traditional industrial robots typically operate in fixed positions with limited mobility. Optimus requires compact, energy-efficient actuators that can provide human-like range of motion while being powerful enough to lift substantial weights. Tesla has developed custom actuators that balance power density, control precision, and energy efficiency.
Balance and Locomotion
Bipedal locomotion is notoriously difficult in robotics. Humans maintain balance through complex proprioceptive systems developed over millions of years of evolution. Tesla has implemented advanced control algorithms that continuously adjust joint torques based on sensory feedback, allowing Optimus to navigate uneven surfaces and maintain balance when pushed or carrying asymmetrical loads.
Dexterity and Manipulation
Human hands represent some of the most complex biomechanical structures in nature. Tesla’s engineers have worked to create hands that can perform a wide range of tasks from delicate manipulation to power gripping. The challenge extends beyond hardware to software algorithms that control grip strength and finger positioning for different objects and tasks.
Neural Networks and Learning
Perhaps the most significant innovation in Optimus is its AI brain. Tesla has leveraged its extensive experience with neural networks from its automotive division. The robot utilizes similar training methodologies to those used for Tesla’s Autopilot system, but adapted for general-purpose robotics. This allows Optimus to:
- Recognize objects in varying lighting conditions
- Navigate dynamic environments safely
- Learn new tasks through demonstration
- Make decisions based on environmental context
Applications and Use Cases
Tesla has outlined several potential applications for Optimus:
Manufacturing
The most immediate application is in Tesla’s own factories. Optimus could handle repetitive tasks like component placement, fastening, and material transport. Unlike traditional industrial robots, Optimus can be quickly reprogrammed or taught new tasks through demonstration, making it suitable for flexible manufacturing environments.
Logistics and Warehousing
The e-commerce boom has created massive demand for warehouse workers. Optimus could potentially address labor shortages by handling package sorting, inventory management, and loading/unloading operations. Its human-like form factor means it can operate in environments designed for human workers without requiring expensive retrofitting.
Elderly Care and Healthcare
As populations age worldwide, the demand for caregivers is rising dramatically. While not intended to replace human caregivers entirely, Optimus could assist with routine tasks like medication reminders, mobility support, and basic health monitoring, allowing human care providers to focus on more complex aspects of care.
Household Applications
Perhaps the most ambitious vision for Optimus is as a household assistant. Tasks like laundry folding, dishwashing, and grocery unpacking require adaptability and dexterity that have challenged robotics engineers for decades. Tesla believes that Optimus’s combination of advanced perception and manipulation capabilities could make it the first truly viable home robot assistant.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite rapid progress, significant challenges remain before Optimus becomes commonplace:
Cost
Early prototypes likely cost hundreds of thousands of dollars to produce. Tesla aims to eventually reduce this to under $20,000 per unit through economies of scale and design optimization, but this remains a challenging target for such a complex device.
Battery Life
Operating a bipedal robot with multiple motors requires substantial energy. Current prototypes can operate for several hours, but practical deployment may require longer operating times or easy charging solutions.
Safety Concerns
A humanoid robot operating in proximity to humans raises obvious safety questions. Tesla has implemented multiple redundant safety systems, including force-limiting actuators, emergency shutdown capabilities, and constant environmental awareness to prevent collisions.
Social Acceptance
Beyond technical challenges, the widespread adoption of humanoid robots requires social acceptance. Tesla has designed Optimus to be functional rather than anthropomorphically “perfect,” aiming for a design that’s approachable without falling into the “uncanny valley” that often makes humanoid robots unsettling.
The Competitive Landscape
Tesla isn’t alone in pursuing humanoid robotics. Boston Dynamics’ Atlas robot has demonstrated impressive agility, while companies like Agility Robotics (Digit) and Figure AI have also made significant strides. Japanese firms like Honda (ASIMO) and SoftBank Robotics have decades of experience in the field.
What distinguishes Tesla’s approach is vertical integration and scale. The company can leverage:
- Experience mass-producing complex electromechanical systems
- Advanced AI capabilities developed for autonomous driving
- Battery technology optimized for energy density and longevity
- A clear path to commercial deployment in its own factories
The Future Outlook
As of late 2024, Optimus remains primarily a research and development project, though Tesla has begun limited deployment in controlled environments within its own facilities. The company has outlined an ambitious roadmap:
- 2025-2026: Expanded deployment within Tesla factories
- 2026-2027: Commercial availability to select industrial partners
- 2027-2028: Potential consumer versions for household applications
Elon Musk has made characteristically bold predictions, suggesting that Optimus could eventually become more significant to Tesla’s business than its automotive division. While such claims should be viewed with healthy skepticism, it’s clear that Tesla is making genuine progress in an exceptionally challenging field.
Conclusion
The Tesla Optimus project represents one of the most ambitious attempts to create a general-purpose humanoid robot in history. By leveraging its expertise in AI, manufacturing, and electrification, Tesla has made remarkable progress in a relatively short time. Whether Optimus ultimately transforms global labor markets as Musk predicts remains to be seen, but the technical innovations emerging from the project are already advancing the field of robotics
Tag – bytetricks
Recent-Post: .NET 10 vs .NET 9 vs .NET 8: Key Differences, Features, and Why You Should Upgrade
Nice post